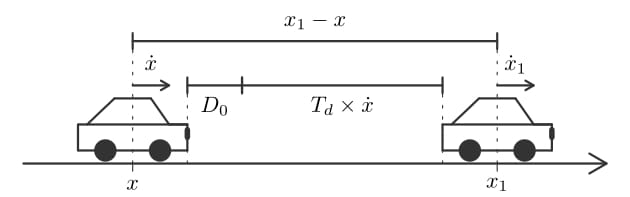
Car-following model and traffic instability
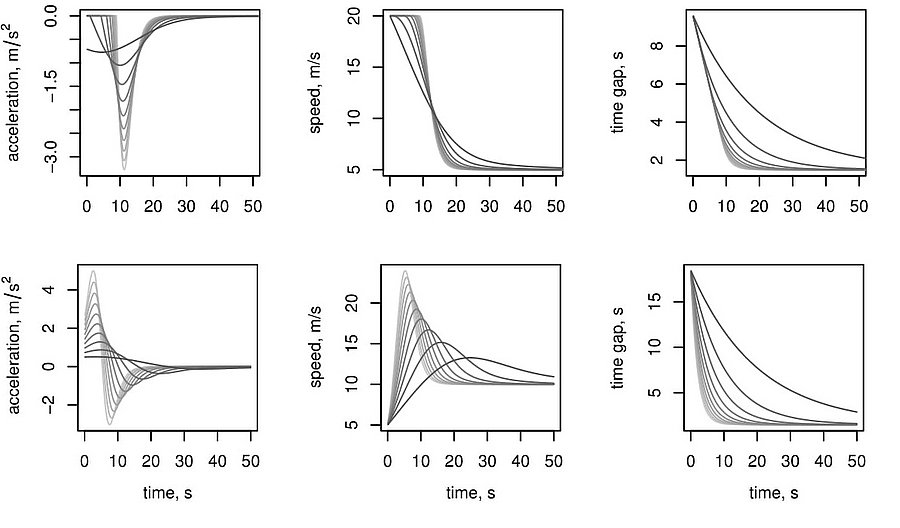
Car-following models, crucial for understanding traffic flow dynamics, have been evolving since the 1950s, offering microscopic insights into vehicle behaviors. These models, based on ordinary, delayed and stochastic differential equations, depict how vehicles adjust speed and acceleration in response to spacing and speed of the preceding vehicle, with applications ranging from adaptive cruise control (ACC) to traffic engineering. The adaptive time gap (ATG) model introduces a safety parameter for time gap regulation, ensuring stable uniform dynamics. The ATG model is a good candidate for ACC systems. The collision-free optimal velocity (CFOV) model is a simplified version of the Optimal Velocity (OV) model by Bando et al. (1995) that mitigates unrealistic collisions and backward movements while describing stop-and-go traffic patterns (see the simulations #1, #2, #3). Derivation of the microscopic CFOV model results in a parabolic convection-diffusion partial differential macroscopic equation while derivation of the ATG models leads to the Lighthill-Whitham-Richards (LWR) macroscopic model.
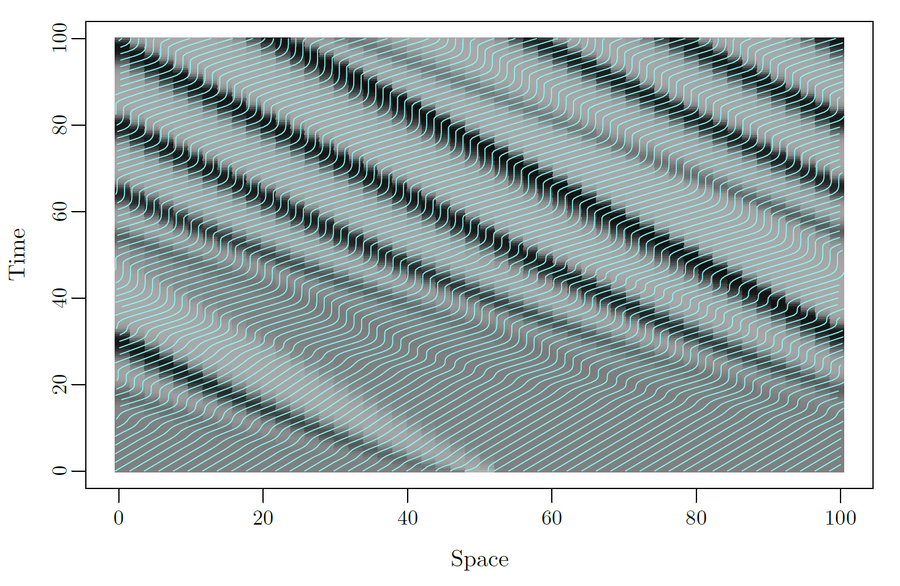
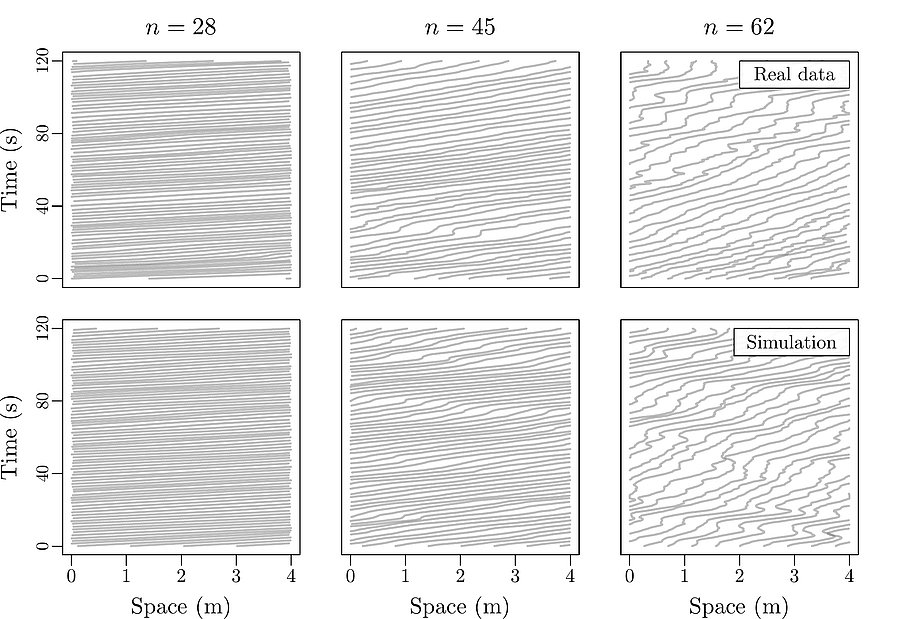
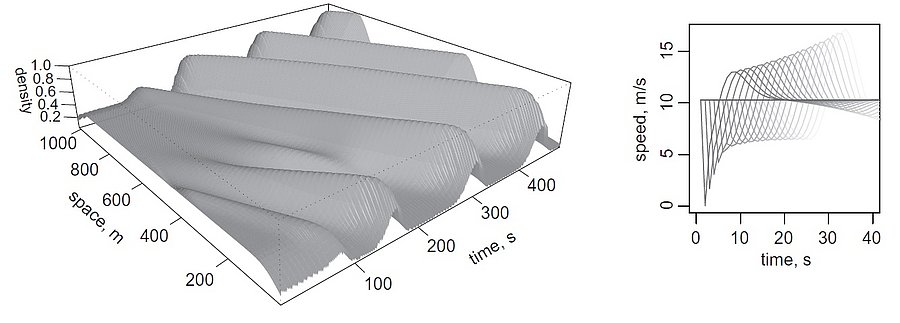
Stop-and-go wave and traffic instability
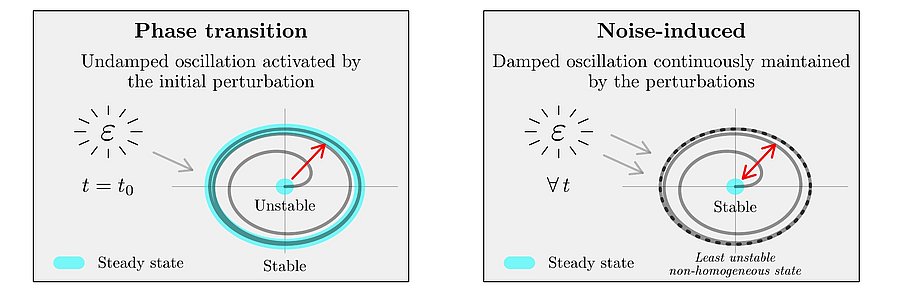
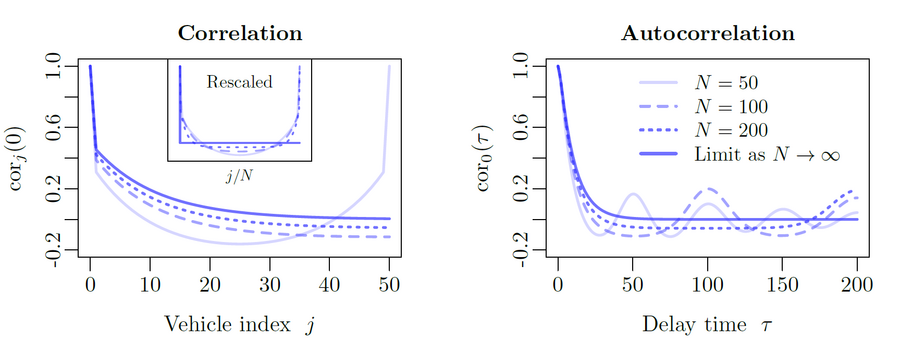
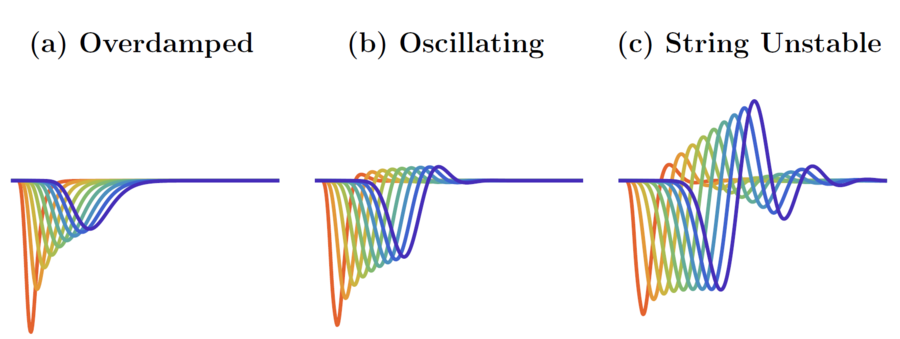
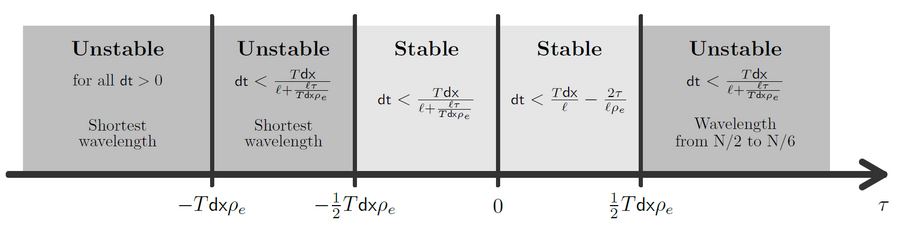
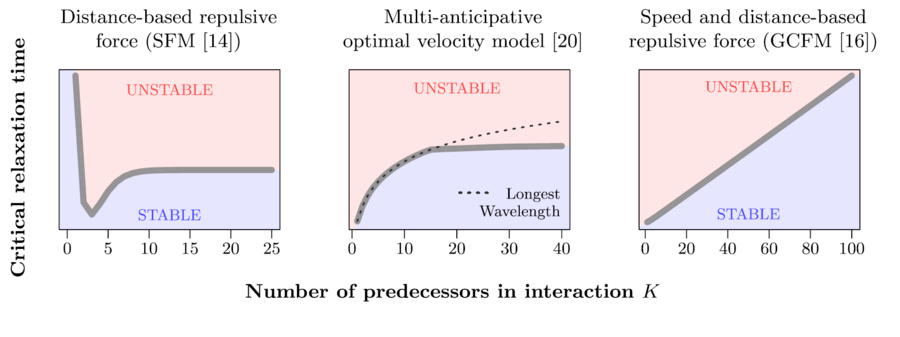
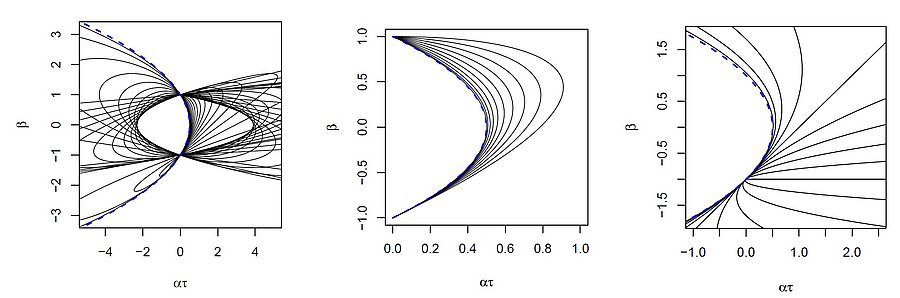
Stop-and-go waves, inherent in congested traffic (see the experiments by Sugiyama et al. or more recently by Stern et al.), pose safety and environmental concerns. Stop-and-go dynamics in single-file motion can emerge due to various factors including delay and latency in nonlinear car-following models, and stochastic noise effects. They induce a phase transition from a laminar traffic to an oscillating traffic with stop-and-go waves, including capacity drop and hysteresis phenomena. Stability analysis of car-following models is vital for ensuring the effectiveness of adaptive cruise control systems. Several recent experiments (see e.g. the experiments by Gunter et al. or the OpenACC experiments) have shown that current ACC systems describe unstable collective behaviors. Local and global (collective) stability considerations essential for understanding oscillating dynamics on infinite or periodic roadways, and . Mathematical techniques range from Laplace transforms for platooning system, to linear algebra with circulant matrix and exponential ansatz for finite periodic and infinite systems, respectively. Inspired by pioneer works with cellular automata models by Nagel, Schreckenberg, and Schadschneider, continuous-time noisy model range from white noise models to colored noises such as Brownian noises given by the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process (see this presentation).
- R. Subaih and A. Tordeux, "Modeling pedestrian single-file movement: Extending the interaction to the follower", Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, vol. 633, pp. 129394, 2024.
- B. Rüdiger, A. Tordeux and B. E. Ugurcan, "Stability analysis of a stochastic port-Hamiltonian car-following model", Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, vol. 57, no. 29, pp. 295203, 2024. IOP Publishing.
- M. Ehrhardt, T. Kruse and A. Tordeux, "The collective dynamics of a stochastic Port-Hamiltonian self-driven agent model in one dimension", ESAIM: M2AN, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 515-544, 2024.
- P. Khound, P. Will, A. Tordeux and F. Gronwald, "The Over-Damped String Stability Condition for a Platooning System", System Theory, Control and Computing Journal, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 12-19, 2023.
- P. Khound, P. Will, A. Tordeux and F. Gronwald, "Unified framework for over-damped string stable adaptive cruise control systems", Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, vol. 148, pp. 104039, 2023. Elsevier.
- J. Cordes, M. Chraibi, A. Tordeux and A. Schadschneider, "Single-File Pedestrian Dynamics: A Review of Agent-Following Models", Bellomo, Nicola and Gibelli, Livio, Eds. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 143-178.
- R. Subaih, M. Maree, A. Tordeux and M. Chraibi, "Questioning the anisotropy of pedestrian dynamics: An empirical analysis with artificial neural networks", Applied Sciences, vol. 12, no. 15, pp. 7563, 2022. MDPI.
- J. Cordes, M. Chraibi, A. Tordeux and A. Schadschneider, "Time-to-collision models for single-file pedestrian motion", Collective Dynamics, vol. 6, pp. 1-10, 2022.
- P. Khound, P. Will, A. Tordeux and F. Gronwald, "The importance of the over-damped string stability criterion for a platooning control system" in 2022 26th IEEE International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), 2022, pp. 1-6.
- M. Friesen, H. Gottschalk, B. Rüdiger and A. Tordeux, "Spontaneous wave formation in stochastic self-driven particle systems", SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, vol. 81, no. 3, pp. 853-870, 2021. SIAM.
- P. Khound, P. Will, A. Tordeux and F. Gronwald, "Extending the adaptive time gap car-following model to enhance local and string stability for adaptive cruise control systems", Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 27, pp. 36-56, 2021. Taylor & Francis.
- J. Wang, M. Boltes, A. Seyfried, A. Tordeux, J. Zhang and W. Weng, "Experimental study on age and gender differences in microscopic movement characteristics of students", Chinese Physics B, vol. 30, no. 9, pp. 098902, 2021. IOP Publishing.
- A. Schadschneider and A. Tordeux, "Noise-induced stop-and-go dynamics in pedestrian single-file motion", Collective Dynamics, vol. 5, pp. 356-363, 2020.
- A. Tordeux, A. Schadschneider and S. Lassarre, "Stop-and-go waves induced by correlated noise in pedestrian models without inertia", Journal of traffic and transportation engineering (English edition), vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 52--60, 2020. Elsevier.
- A. Tordeux, J. Lebacque and S. Lassarre, "Robustness analysis of car-following models for full speed range ACC systems" in Traffic and Granular Flow 2019, Springer, 2020, pp. 571-581.
- J. Cordes, A. Schadschneider and A. Tordeux, "The trouble with 2nd order models or how to generate stop-and-go traffic in a 1st order model" in Traffic and Granular Flow 2019, Springer, 2020, pp. 45--51.
- J. Wang, M. Boltes, A. Seyfried, A. Tordeux, J. Zhang, V. Ziemer and W. Weng, "Influence of gender on the fundamental diagram and gait characteristics" in International Conference on Traffic and Granular Flow, 2019, pp. 225-234.
- A. Tordeux, A. Schadschneider and S. Lassarre, "Noise-induced stop-and-go dynamics" in International Conference on Traffic and Granular Flow, 2019, pp. 337-345.
- A. Tordeux, G. Costeseque, M. Herty and A. Seyfried, "From traffic and pedestrian follow-the-leader models with reaction time to first order convection-diffusion flow models", SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, vol. 78, no. 1, pp. 63-79, 2018. SIAM.
- A. Tordeux, M. Chraibi, A. Schadschneider and A. Seyfried, "Influence of the number of predecessors in interaction within acceleration-based flow models", Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, vol. 50, no. 34, pp. 345102, 2017. IOP Publishing.